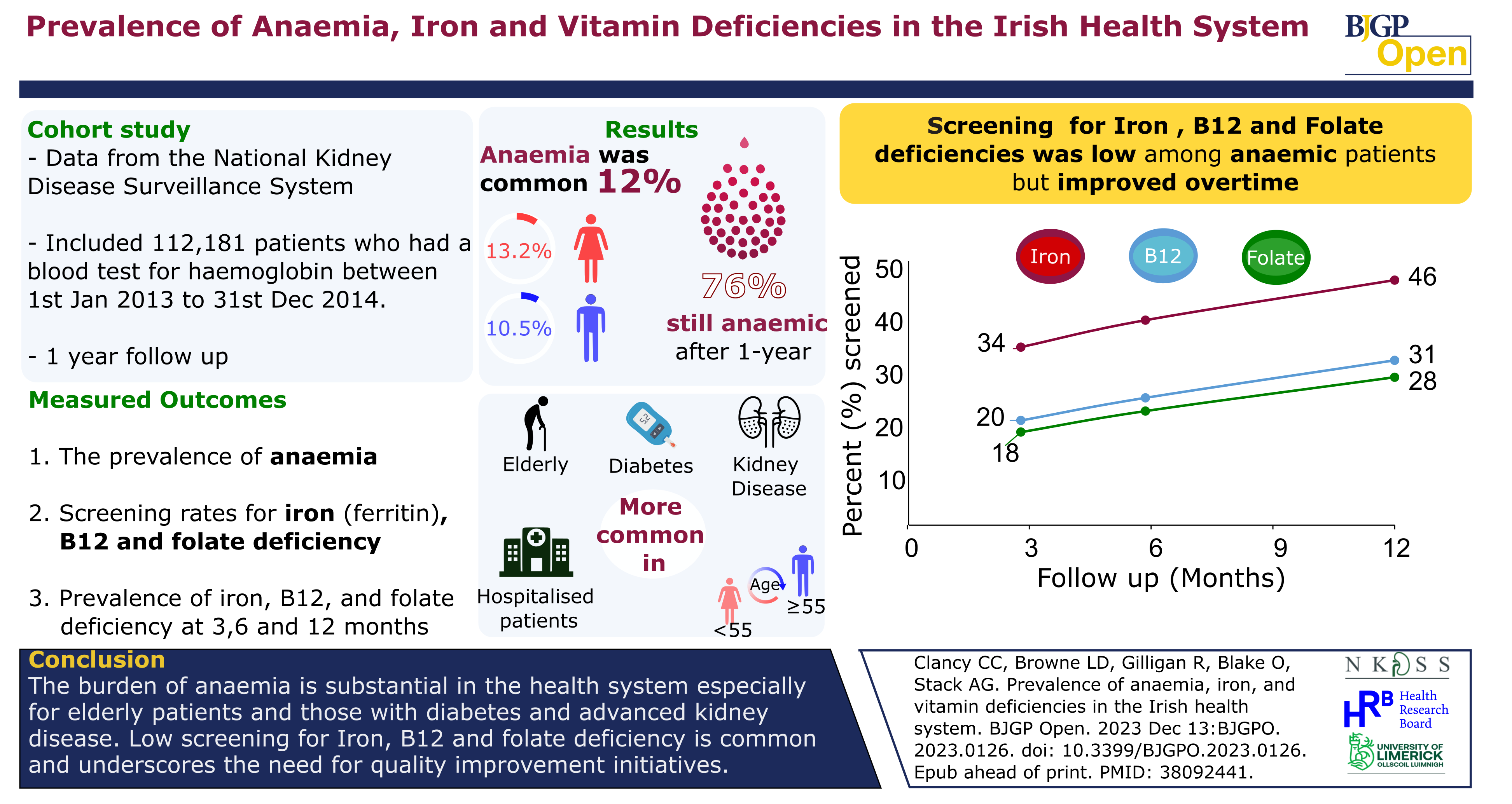
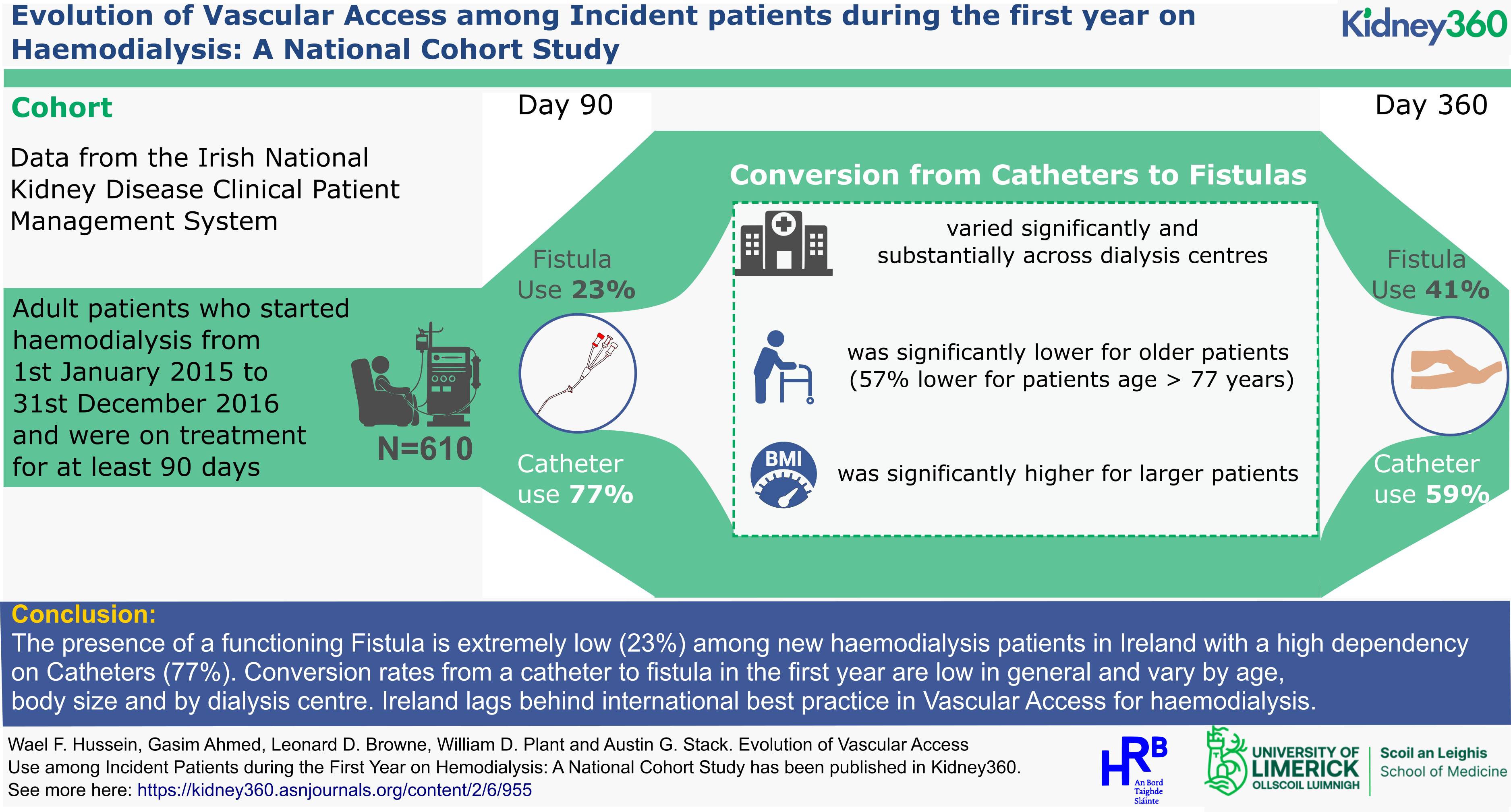
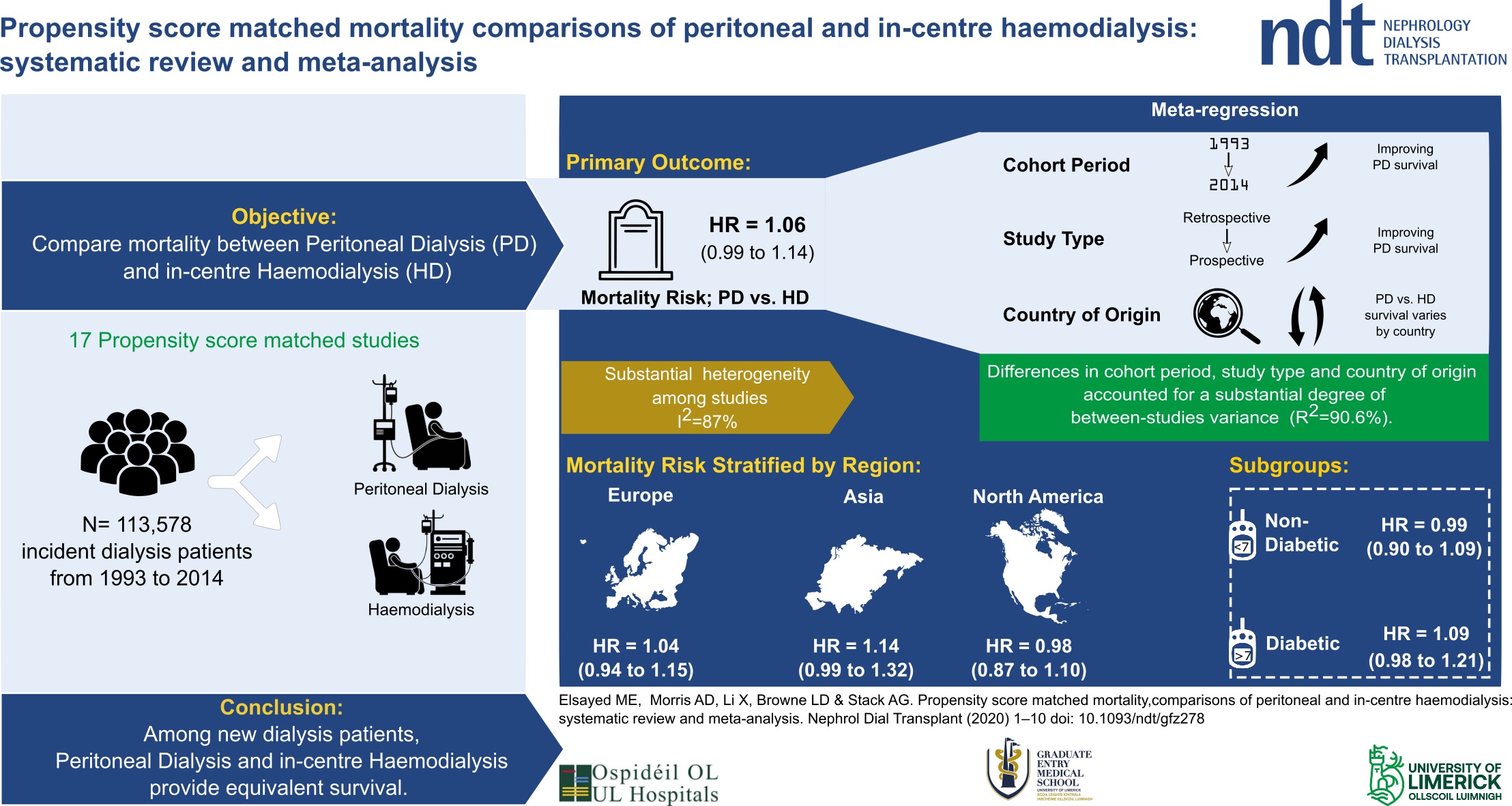
High prevalence of anaemia in CKD but low testing rates for Iron, B12 and folate deficiency
A new study by researchers at University of Limerick has found high rates of anaemia among patients in the health system, while screening for common causes is low. The research study carried out by a team at University of Limerick School of Medicine found that substantial numbers of men and women in the health system had anaemia, the presence of which is strongly associated with high rates of hospitalisation, death, and poor quality of life.
Continue Reading